Unit Vocabulary-
Nota bene - I included some extra pictures because I thought they were too hilarious and/or relevant to choose from. There are still pictures to meet the requirement of the assignment, though.
Nota bene - I included some extra pictures because I thought they were too hilarious and/or relevant to choose from. There are still pictures to meet the requirement of the assignment, though.
The list is below:
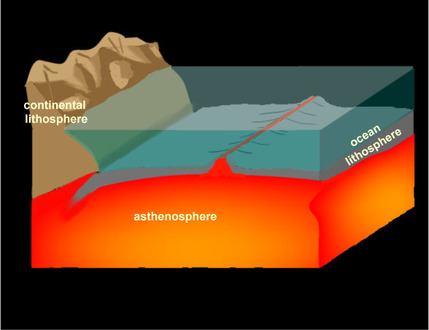
Tectonic Cycle - crust being created and destroyed
Deposition - accumulation of eroded material

Cation Exchange Capacity - ability of soil to absorb and release positively charged mineral ions
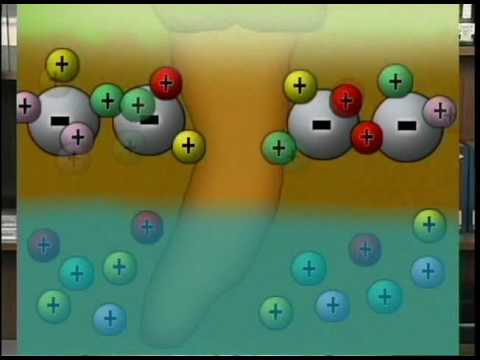





Cation Exchange Capacity - ability of soil to absorb and release positively charged mineral ions





Human Impact: Humans help cause soil degradation, erosion, and chemical weathering through many activities. Overfarming, construction, and logging get rid of plants that helped keep the soil there in place. Without them there, the soil erodes taking the fertility mean it. This in turn means that humans are affected by lower crop yield and even dust bowl conditions which we try to fix with nitrogenated and phosporated fertilizer that runs off (causing algal blooms and hypoxia) even quicker because there's nothing to keep the soil in which it is poured from eroding away. Through mining, humans also lay waste to large stretches of Earth's surface. Strip mining leaves strips of bare earth, decimating the ecosystems that were there. Open pit mining often uses acidic slurry that infiltrates groundwater and runsoff harming environments along the way. Anthropogenic sulfur emissions form acid rain that more quickly chemically erodes rocks, especially building materials like limestone; the acid rain harms human buildings made of rock. Earthquakes and volcanoes harm humans and their habitation so cities near faults are more likely to build buildings to be adapted to earthquakes. Volcanoes erupt and destroy populations, but also form islands for human habitation such as Hawai'i. Oceanic plate movement can result in terrible tsunamis that wash away entire cities and cause a significant amount of human death.
Environmental Impact: Soil degradation makes it much harder for plants to grow and for the animals that survive on those plants to survive, disrupting the whole food chain. Not only is this detrimental to the whole ecosystem, but a keystone species which has a disproportional effect on the ecosystem, could be harmed leading to a great decrease in biodiversity. Strip mining and chemical weathering have similar deleterious effects on ecosystems. The machinery used in these operations also contributes to greenhouse gas accumulation and pollution. The resulting loss of biodiversity is very harmful, especially since biodiversity is key to overall genetic diversity and therefore survivability. Volcanoes and earthquakes can also harm ecosystems. Primary succession occurs after a volcano eruption so a new ecosystem forms eventually. Tsunamis caused by oceanic tectonic plate movement can wash away unadapted species or their food sources, causing a change in ecosystem populations or washing the ecosystem away entirely.
Economic Impact: Mining is a very lucrative industry, especially as the world becomes more reliant on fossil fuels. Strip, open pit, and mountain top mining all greatly change the environment but also create a large amount of jobs and revenue. Placer mining is less disruptive but still economically significant. Earthquake, volcano, and tsunami can cause a significant amount of economic loss by destroying cities and decreasing the labor force, necessitating extensive rebuilding. Soil degradation also hurts crop yield and requires to pay greater expenses for more fertilizer to try and make the soil viable.
Governmental Legislation - The Federal Land and Policy Act of 1976 prevents unnecessary degradation of federal lands, putting a limit on mining. The Clean Water Act of 1972 establishes standards for surface water to ensure it doesn't get too polluted by things like fertilizer and slurry runoff borne of eroded soil and open pit mining. The city of Denton recently passed a law to ban fracking within the city limits due to a lack of community benefit and an abundance of harms, such as environmental disruption. Fracking is unlike the previously discussed mining techniques because it is used to obtain natural gas but has detrimental effects just as they do.