Unit Vocabulary-
CBR - number of births per year per 1000 people
CDR - number of deaths per year per 1000 people
TFR - total fertility rate, the average number of children a woman will have
Replacement Level Fertility - TFR necessary for a stable population, normally about 2.1
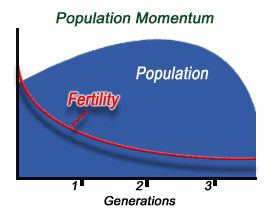
Population Momentum - the tendency of a population to keep growing even if there was an immediate decrease in crude birth rates ex. China right now
Family Planning - using birth control and increased education to decide when to start a family (usually later in life), characteristic of late stages of demographic transition
Affluence - qualitative measure of quality of life especially applied to materialistic standing
IPAT equation - Impact = population x affluence x technology; qualitative measure of environmental impact
GDP - gross domestic product, measure of economic wealth, 4 parts : consumer spending, government spending, exports minuse imports, and investments
Population Pyramid- no definition, just include an example of what a pyramid looks like for a country experiencing a high growth rate, stable growth, and a declining population.
High growth Stable Growth Declining
Making Connections-
There is not much expected environmental impact in stage 1 since the population is still fairly small and economic activity mostly consists of subsistence farming without much government infrastructure that disrupts the environment. This is because of the high CBR and CDR. The greatest environmental impact would probably be disposing of all the corpses, whether by burial, cremation, or some other unspecified method. There would be much greater environmental impact in stage 2 since CDR would greatly decrease as a result of better medicine, sanitation, and technology, which means a huge increase in population. The greater number of people puts greater pressure on the environment in terms of space and resources like food, water, and lumber. This is also typically when industrialization occurs, with an emphasis on primary and secondary sector activities like agriculture and mining. The industrial activity ravages the environment as it expands with pollution and damaged landscapes, especially since the lower standard of living and push for economic growth results in laxer environmental concerns. In stage 3, population growth begins to stabilize and environmental regulations improve as a result of higher standards of living which decrease environmental impact to an extent, the but the great population, and high levels of affluence and technology still result in a huge environmental impact. Stage 4 countries also have a large amount of environmental impact because of affluence and technology, but the population declines which results in a little bit less of an environmental impact than before.
Current Event-
http://www.theguardian.com/world/2014/nov/13/india-population-growth-policy-problems-sterilisation-incentives-coercion
The article talks about the massive sterilization going on in India, mainly in females since it is still considered culturally unacceptable for males to get vasectomies. It goes on to talk about the massive incentives in places, as well as the lack of family planning and contraceptives since emphasis is placed on sterilization, the cheaper option. While many women, almost 40%, have undergone the procedure indicating a high success rate, this is problematic for many reasons. Reliance on sterilization has decreased the push for education on contraceptives and family planning in rural India which means women are not necessarily educated about their choices and that it's a temporary fix; without a cultural change, the problem will still exist. It is also problematic because of the gender imbalance; women are disproportionately expected to get the procedure done, evidence of a perceived inferiority of women and reluctance to educate women. The sterilizations also often involve the coercion of women, whether by incentives or family members, which is extremely harmful to autonomy.
Big Picture Reflection- This is where you will make the four BIG PICTURE connections to the ENTIRE UNIT. Please tie in information you learned in your reading, from completing your assignments, the documentary we watched and from your current event. There is not an exact length that I am expecting other than it should definitely be at least a paragraph for each section, should be thorough and show understanding of the topic.
Human Impact: As populations, technology, and affluence increase, so does the impact on the environment as a general trend. Advances in technology can, however, lead to innovations that actually help conserve environmental resources. The increase in population and affluence are directly correlated to the stages of the demographic transition model. The environment affects humans by dictating what economic activity can occur and how many humans can live there. The increasing demand for fossil fuels and urbanization have contributed to increased environmental distress.
Environmental Impact: There is less environmental impact when there aren't as many humans and when their lifestyles aren't too affluent, corresponding to the earlier stages of the demographic transition model. The environment limits the activities and amount of humans that can exist, influencing the demographic transition model as well. Places with abundant resources and favorable climates have gone through demographic transition earlier than nations that have less favorable climates and less resources. As affluence and technology increase, though, there is greater importance placed on finding more environment friendly alternatives. Increased populations and resource consumption lead to the destruction of habitats, pollution, and a resulting decrease in biodiversity which is harmful to the resilience of ecosystems.
Economic Impact;
A younger, growing population characteristic of stage 2 and stage 3 of the DTM correspond to greater economic well-being since there is a greater, growing workforce. New industries also arise because of the ability to focus on things besides immediate survival and the increased sanitation, medicine, and technology. As quality of life increases, even more industries grow because there is now a market for more things that make life easier. GDP generally increases as countries go through the demographic transition model, though stage 4 countries with a declining population often face the problem of balancing an aging retiring population on a smaller work force.
Government Legislation: Countries with unchecked population growth often institute measures to decrease CBR and TFR. China instituted a 1 child policy that gave benefits and incentives to couples with only one child and penalized couples with more than one child. India has tried to institute mass sterilization which has resulted in decreased emphasis on education. Non governmental organizations (NGOs), however, have tried to fill this gap and provide education and contraceptives to rural regions in India and other countries. They have also tried to address the gender disparity and provide education to women as multiple studies and trends have shown that increased female literacy correlates to decreased fertility rates. The government of Nigeria, the country with the highest fertility rate in the world as of 2011, has been investing in birth control and family planning to try and decrease birth rates.
In more developed countries, there are more restrictions on economic activity. Just this year, the EPA prohibited the construction of an Alaskan mine because of the danger posed to a nearby Bristol Bay ecosystem. In contrast, mining activity is virtually unrestricted and unregulated in places like Cuba, Guyana, and the Philippines. This can be attributed to the prioritization of economic development in developing countries and increased environmental regulations in developed countries as a result of increased standards of living and education pushing corporations to less regulated areas where they can turn more profit.